×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Volkswagen Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
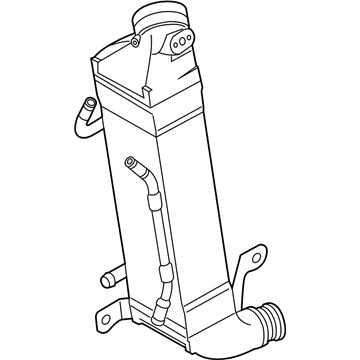
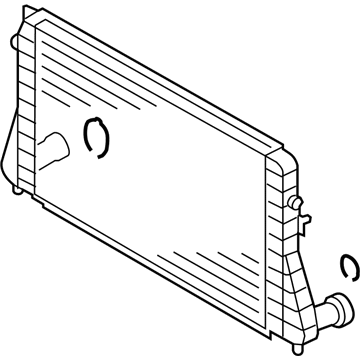
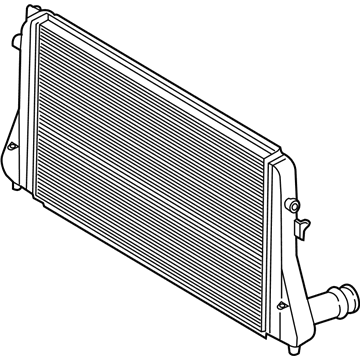
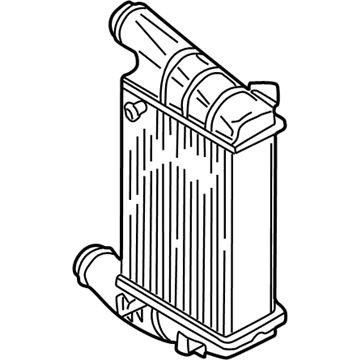
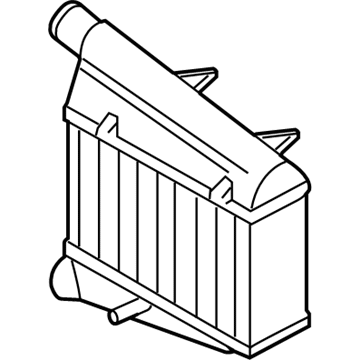
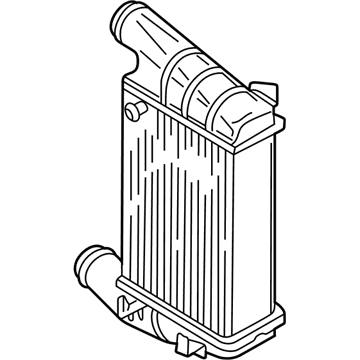
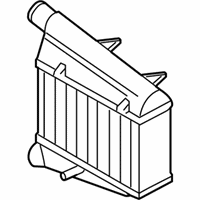
Genuine Volkswagen Passat Intercooler
Front Intercooler- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
7 Intercoolers found
Volkswagen Passat Intercooler Part Number: 3AA-145-805-B
$430.04 MSRP: $587.49You Save: $157.45 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Intercooler Part Number: 3C0-145-805-R
$445.29 MSRP: $608.32You Save: $163.03 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Intercooler Part Number: 1K0-145-803-CG
$497.14 MSRP: $679.15You Save: $182.01 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Intercooler Part Number: 3B0-145-805-H
$498.31 MSRP: $680.75You Save: $182.44 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Intercooler Part Number: 3B0-145-805-D
$560.47 MSRP: $765.67You Save: $205.20 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Intercooler Part Number: 3A0-145-805-B
$270.11 MSRP: $369.00You Save: $98.89 (27%)Volkswagen Passat Intercooler Part Number: 058-145-805-A
Volkswagen Passat Intercooler
Choose OEM Intercooler for superior quality and long-lasting durability. They match the Volkswagen's factory specifications exactly and pass strict quality control. If you plan to replace Intercooler on your Passat, put OEM at the top of your list. You'll get the right fit, reliable performance, and peace of mind. We stock an extensive inventory of genuine Volkswagen Passat parts. It is easy to find what you need. You will love our competitive prices that help you save. No more hassle with returns or guesswork. Every part includes a warranty straight from the manufacturer. Get trusted quality, strong durability, and real value today.
Volkswagen Passat Intercooler Parts and Q&A
- Q: How to diagnose and replace a turbocharger and intercooler on Volkswagen Passat?A:The turbocharger is a delicate device that may be seriously damaged by improper lubrication or introduction of foreign matter into the air intake duct, and the results are usually manifested by a malfunctioning engine, blue/grey smoke in the exhaust, or unusual sounds. In order to diagnose possible problems, check the intake air duct whether it is loose, ruined, in any case there are no obstructions in air intake system and also look at the system vacuum hoses, wiring and electrical connectors whether they are damaged or corroded. Also check that the wastegate actuator connection is not binding and check the exhaust system, lubricating oil supply line and drain back line, and coolant supply line and coolant return line has no damages or blockages. In case of replacement, empty the cooling system, lift the car up and take out the engine compartment cover. Disconnect the air conditioning compressor, without disconnecting the refrigerant hoses and remove the turbocharger support bracket and the air inlet and outlet ducts, oil return pipe and oil supply pipe. Also, detach the vacuum hose to the wastegate actuator, the air filter housing and air filter duct, and loosen the crankcase ventilation hose. Once the turbocharger has been removed, it must be installed in reverse sequence, with all the gaskets, seals and nuts turned over, and the mounting bolts of the turbocharger fitted to the correct torque. Remember to take off the fuel pump fuse before proceeding to start the engine until the pressure of oil develops. In the case of the intercooler, lift the vehicle up, undo the engine compartment undercover, undo the air deflector, and undo the upper and lower air ducts and remove the mounting bolts after which the intercooler can be removed and re installed in the same sequence.
Related Volkswagen Passat Parts
Browse by Year
2022 Intercooler 2021 Intercooler 2020 Intercooler 2019 Intercooler 2018 Intercooler 2017 Intercooler 2016 Intercooler 2015 Intercooler 2014 Intercooler 2013 Intercooler 2012 Intercooler 2010 Intercooler 2009 Intercooler 2008 Intercooler 2007 Intercooler 2006 Intercooler 2005 Intercooler 2004 Intercooler 2003 Intercooler 2002 Intercooler 2001 Intercooler 2000 Intercooler 1999 Intercooler 1998 Intercooler 1997 Intercooler 1996 Intercooler