×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Volkswagen Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
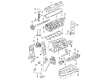
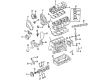
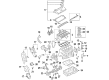
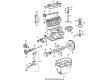
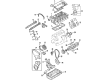
Genuine Volkswagen Passat Valve Spring
- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
11 Valve Springs found
Volkswagen Passat Valve Springs Part Number: 078-109-623-A
$28.34 MSRP: $47.23You Save: $18.89 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Valve Springs Part Number: 028-109-623-A
$7.54 MSRP: $12.36You Save: $4.82 (39%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Valve Springs Part Number: 038-109-623-F
$35.63 MSRP: $59.38You Save: $23.75 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Valve Springs Part Number: 03H-109-623-C
$7.56 MSRP: $12.41You Save: $4.85 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Rotor Part Number: 078-109-633-A
$19.08 MSRP: $31.27You Save: $12.19 (39%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Valve Springs Part Number: 038-109-633
$23.78 MSRP: $38.98You Save: $15.20 (39%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Intake Valve Part Number: 06D-109-601-M
$61.87 MSRP: $86.65You Save: $24.78 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Exhaust Valve Part Number: 06D-109-611-H
$61.87 MSRP: $86.65You Save: $24.78 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Valve Springs Part Number: 078-109-623-B
$82.10 MSRP: $114.98You Save: $32.88 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Valve Springs Part Number: 021-109-633
$3.34 MSRP: $4.57You Save: $1.23 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Passat Exhaust Valve Part Number: 021-109-623-L
$5.93 MSRP: $8.10You Save: $2.17 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Volkswagen Passat Valve Spring
Choose OEM Valve Spring for superior quality and long-lasting durability. They match the Volkswagen's factory specifications exactly and pass strict quality control. If you plan to replace Valve Spring on your Passat, put OEM at the top of your list. You'll get the right fit, reliable performance, and peace of mind. We stock an extensive inventory of genuine Volkswagen Passat parts. It is easy to find what you need. You will love our competitive prices that help you save. No more hassle with returns or guesswork. Every part includes a warranty straight from the manufacturer. Get trusted quality, strong durability, and real value today.
Volkswagen Passat Valve Spring Parts and Q&A
- Q: How can broken Valve Spring, Valve Spring Retainer and Valve Stem Oil Seal be replaced without removing the cylinder heads for V6 engines on Volkswagen Passat?A:Defective valve stem seals and broken valve springs can be changed by removing the Cylinder Heads, normally with 2 special tools and a source of compressed air. Start with the removal of the valve cover, Camshaft, and lifters, followed by the removal of the spark plug in the affected cylinder or all the spark plugs in case of replacing all the valve stem seals. Rotate the crankshaft until the piston reaches TDC where the first cylinder starts and the firing sequence should be followed, or in DOHC engines, the second cylinder should start. Insert a threaded air hose adapter into the spark plug hole and attach it to a source of compressed air and spray air into the engine to hold the valves open. Wrap rags on stuff around the valve holes to allow nothing to fall into it then carefully strike the valve spring retainers with a blow to sever the connection between the retainers and the keepers. Compress the spring using a valve spring compressor and remove the keepers using pliers or magnet, be sure to use the matching type of compressor; Import type. Unscrew the valve spring and retainer, and be careful to leave the valve held in the closed position by air pressure so as not to break it. Take off old valve stem seals, be careful of the intake and exhaust seal differences and press the valve stem in place with a rubber band or tapes and then release the air pressure. Check the valve stem, make sure that it slides freely in the guide; otherwise the head must be taken off to be repaired. Once more, apply air pressure to hold the valve, rub the stem with engine oil and fit a fresh seal, being careful that a protective sleeve is put on to prevent damage. Install the valve spring and retainer, push the spring and fit the keepers with grease to keep in place. Take the spring tool off, disconnect the air hose and take off the adapter. Lastly, re-fit the camshaft, lifters, Timing Belt, valve cover, spark plug(s), and wires, and start engine and investigate any oil leaks and abnormal sounds.
Related Volkswagen Passat Parts
Browse by Year
2018 Valve Spring 2017 Valve Spring 2016 Valve Spring 2015 Valve Spring 2014 Valve Spring 2013 Valve Spring 2012 Valve Spring 2010 Valve Spring 2009 Valve Spring 2008 Valve Spring 2007 Valve Spring 2006 Valve Spring 2005 Valve Spring 2004 Valve Spring 2003 Valve Spring 2002 Valve Spring 2001 Valve Spring 2000 Valve Spring 1999 Valve Spring 1998 Valve Spring 1997 Valve Spring 1996 Valve Spring 1995 Valve Spring 1994 Valve Spring 1993 Valve Spring 1992 Valve Spring 1991 Valve Spring 1990 Valve Spring