×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Volkswagen Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
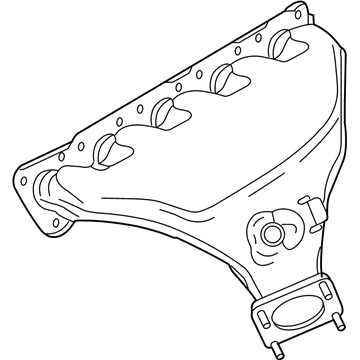
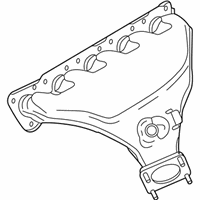
Genuine Volkswagen Rabbit Exhaust Manifold
Engine Exhaust Manifold- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
4 Exhaust Manifolds found
Volkswagen Rabbit Exhaust Manifold Part Number: 07K-253-031-H
$414.45 MSRP: $566.19You Save: $151.74 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Rabbit Manifold Part Number: 067-253-031-AG
$314.03 MSRP: $429.00You Save: $114.97 (27%)Volkswagen Rabbit Manifold Part Number: 055-253-031-T
$321.35 MSRP: $439.00You Save: $117.65 (27%)Volkswagen Rabbit Valve Part Number: 068-100-104-J
$0.01Ships in 1-2 Business Days
Volkswagen Rabbit Exhaust Manifold
Choose OEM Exhaust Manifold for superior quality and long-lasting durability. They match the Volkswagen's factory specifications exactly and pass strict quality control. If you plan to replace Exhaust Manifold on your Rabbit, put OEM at the top of your list. You'll get the right fit, reliable performance, and peace of mind. We stock an extensive inventory of genuine Volkswagen Rabbit parts. It is easy to find what you need. You will love our competitive prices that help you save. No more hassle with returns or guesswork. Every part includes a warranty straight from the manufacturer. Get trusted quality, strong durability, and real value today.
Volkswagen Rabbit Exhaust Manifold Parts and Q&A
- Q: How to diagnose and replace the Exhaust Manifold, Intercooler and Turbocharger on Volkswagen Rabbit?A:The turbocharger is a delicate part that may become incurably damaged due to lack of lubrication or the entry of foreign materials into the air intake duct, failure is manifested by poorly functioning engines, blue/ gray smoke, or strange sounds. The initial symptoms of suspected turbocharger failure to be tested are: the duct of intake air should be loose or damaged, no restriction done on air intake system, damage on the vacuum hoses and wiring, linking of actuator on the wastegate should not be binding and inspection of the exhaust system, supply of lubricating oil, drainback lines and coolant supply and return lines. Without detection of the problem by such checks, full diagnosis might be necessary using special techniques and equipment in a dealer service department or in a repair facility with adequate facilities. In replacing the turbocharger, warm the engine then drain the oil, disconnect the battery, loosen the right front wheel bolts, lift the vehicle safely and remove the right front wheel. Take away splash shield under the vehicles, engine cover, side inner fender liners, charge air hose, heater hose, coolant hose, electrical connectors, exhaust manifold heat shield, PCV fresh air hose and other parts that are attached to the turbocharger. Disassemble the exhaust manifold/turbocharger unit and am sure to turn the engine if removal is required. During installation of the new assembly, lubricate all fasteners using anti-seize compound, change seals and gaskets and ensure the correct alignment of the exhaust system. Fill up engine oil and refill engine coolant then start the engine and leave it to idle a minute to make sure there is enough oil to the turbocharger. In the case of charge air cooler, lift up vehicle, lift lower splash shield, engine cover, front bumper cover and empty out cooling system. Unattach the right charge air hose, cooling fan shroud and radiator, then empty the charge air cooler and other related parts, being careful to replace any damaged ducts, hoses or clamps during re-fitting.