×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Volkswagen Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
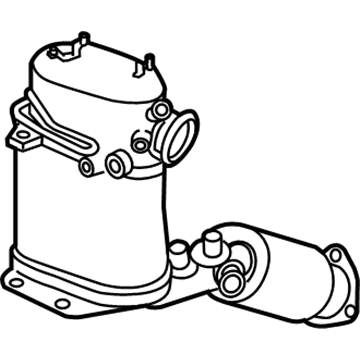
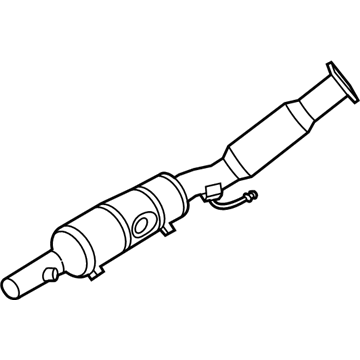
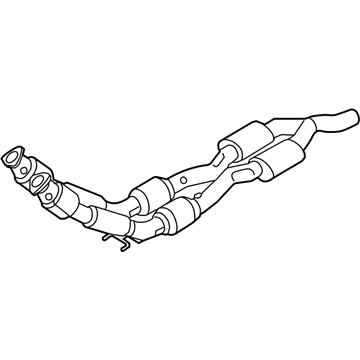
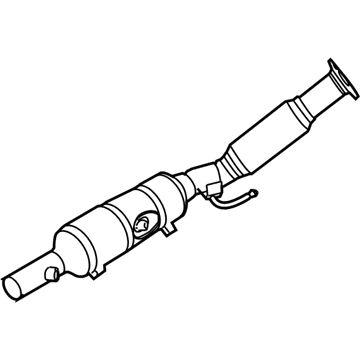
Genuine Volkswagen Catalytic Converter
Cat. Converter- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
161 Catalytic Converters found
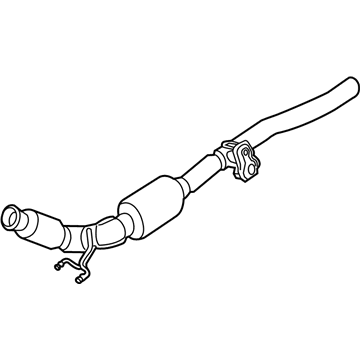
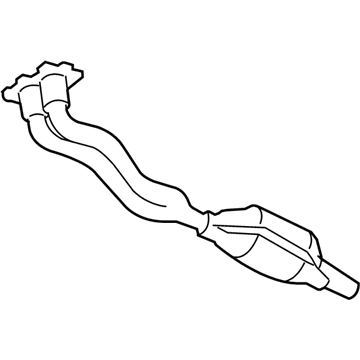
Volkswagen Crossover Pipe Part Number: 7B0-253-201-A
$190.51 MSRP: $266.81You Save: $76.30 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pipe; Crossover Pipe
- Replaces: 7B0-253-201
Volkswagen Crossover Pipe Part Number: 7B0-253-301
$614.01 MSRP: $838.81You Save: $224.80 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pipe; Crossover Pipe
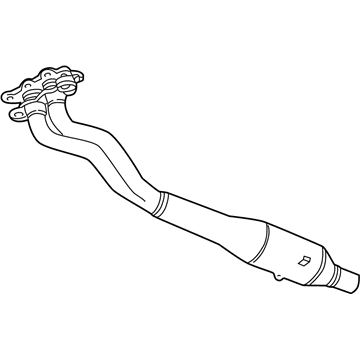
Volkswagen Front Pipe Part Number: 7B0-253-091-J
$608.34 MSRP: $831.07You Save: $222.73 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Exhaust Pipe; Converter & Pipe, Front Pipe
- Replaces: 7B0-253-091-B, 7B0-253-091-A, 7B0-253-091-G, 7B0-253-091-D, 7B0-253-091-E, 7B0-253-091-H, 7B0-253-091-F
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Part Number: 7B0-253-019-N
$1456.17 MSRP: $1989.30You Save: $533.13 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Exhaust Manifold; Catalytic Converter, Manifold
- Position: Left
- Replaces: 7B0-253-019-E, 7B0-253-019-J, 7B0-253-019-K, 7B0-253-019-F, 7B0-253-019-L, 7B0-253-019-H, 7B0-253-019-G, 7B0-253-019-M
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Part Number: 7B0-254-502-A
$1948.51 MSRP: $2661.90You Save: $713.39 (27%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Catalytic Converter
- Replaces: 7B0-254-502
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Part Number: 1K0-254-401-R
$141.53 MSRP: $169.90You Save: $28.37 (17%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Converter & Pipe
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Part Number: 561-254-400-A
$3069.48 MSRP: $3594.24You Save: $524.76 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Catalytic Converter
Volkswagen Converter & Pipe Part Number: 1J0-254-506-R
$512.40 MSRP: $600.00You Save: $87.60 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic
- Replaces: 1J0-254-504-R
Volkswagen Exhaust Pipe Part Number: 5Q0-254-300-P
$585.53 MSRP: $685.63You Save: $100.10 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Exhaust Pipe
- Replaces: 5Q0-254-300-J
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Part Number: 1K0-254-401-N
$652.70 MSRP: $764.28You Save: $111.58 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Part Number: 1K0-254-308-N
$578.28 MSRP: $677.14You Save: $98.86 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Catalytic Converter
- Replaced by: 1K0-254-309-C
Volkswagen Exhaust Pipe Part Number: 1K0-254-309-C
$578.28 MSRP: $677.14You Save: $98.86 (15%)Product Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Converter & Pipe, Exhaust Pipe
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Part Number: 5C0-253-059-AH
$767.75 MSRP: $899.00You Save: $131.25 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Catalytic Converter
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Part Number: 1HM-131-701-RX
$874.14 MSRP: $1023.58You Save: $149.44 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Catalytic Converter
Volkswagen Front Pipe Part Number: 1J0-254-508-QX
$901.57 MSRP: $1055.70You Save: $154.13 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Front Pipe
- Replaces: 1J0-254-505-X, 1J0-253-058-PX
Volkswagen Front Pipe Part Number: 1J0-254-508-G
$948.54 MSRP: $1110.71You Save: $162.17 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Converter & Pipe, Front Pipe
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Part Number: 561-253-053-A
$2786.15 MSRP: $3262.47You Save: $476.32 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Part Number: 5C0-253-059-AM
$979.10 MSRP: $1146.48You Save: $167.38 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Catalytic Converter, Front Pipe
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Part Number: 561-254-500-D
$1109.58 MSRP: $1299.27You Save: $189.69 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic; Catalytic Converter, Converter & Pipe
- Replaces: 561-254-500-A, 561-254-500-B
Volkswagen Converter & Pipe Part Number: 1K0-254-511-N
$1158.79 MSRP: $1356.90You Save: $198.11 (15%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Catalytic
| Page 1 of 9 |Next >
1-20 of 161 Results
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter
A total system failure could result from a malfunctioning Volkswagen Catalytic Converter, reducing driving comfort and posing a danger. It is for this reason that you should conduct regular inspections and replace such components in good time to enable your car to run smoothly and safely. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) Volkswagen Catalytic Converters are perfect for motorists because they are the best quality parts produced as per the manufacturer's specifications; hence, they perform well and are reliable too, thus helping to retain the car's initial functionality as well as safety features. At VWPartsGiant.com, our genuine Volkswagen Catalytic Converter supply indicates how much we care about the health of your vehicle. Additionally, our stock is vast, so every product will be easily accessible to you for finding and swapping without fear of making mistakes. With our user-friendly online catalog, it takes no time to identify the right spare part. Therefore, convenience accompanies servicing or maintaining a motorcar. You can rely on our OEM Volkswagen Catalytic Converter to sustain the performance of your automobile.
Volkswagen Catalytic Converter Parts and Q&A
- Q: How to remove the front exhaust pipe and catalytic converter as a single assembly on Volkswagen Jetta?A:The catalytic converter and the front exhaust pipe are between one component. Start by taking off the engine cover. Weakening procedure- Loosen the right-front wheel bolts and then raise the front of the vehicle and place it on jackstands. The second step is to remove the under-vehicle splash shield. Lose the inner fender liner to the right, as needed. The next step is to take out the upstream and downstream oxygen sensors of the catalytic converter. Should you have it, take out the heat shield at the turbo charger. Afterward, remove the fasteners / clamps, which hold the front exhaust pipe with the catalytic converter to a manifold, cylinder head and or turbocharger. Unscrew the support ejaculatory bracket bolts and eliminate the support bracket. Disassemble the connections between the clamps which hold the catalytic converter to the rear exhaust and take out the catalytic converter along with the front exhaust pipe. Get rid of the old flange gasket and clamps. To install, follow the reverse procedure of the removal, and make sure to apply new gaskets and self-locking nuts when securing all the fasteners.
- Q: Should you consult a dealer service department before replacing a catalytic converter due to federally mandated warranty coverage on Volkswagen Passat?A:Since there is a Federally required warranty on the emissions-related parts such as the catalytic converter, it would be prudent to contact a dealer service department before replacing the converter at your own charge. An emission control device installed in the exhaust system to reduce the pollutant level in the exhaust gasses is the catalytic converter in which a three-way catalyst design is used with the coating of platinum and rhodium to minimize the amount of oxides of nitrogen, hydrocarbons, and carbon monoxide in the exhaust gasses. Catalytic converter testing equipment is also expensive and advanced and in case of a suspected malfunction, one should visit a dealer or a certified emissions testing facility and have his diagnosis and repair. When servicing underbody parts, inspection of converter leaks, corrosions, dents and other damages, inspection of welds and flange bolts between converter and exhaust system, and replacement of converter in case of damages. A plugged catalytic converter may be investigated with the help of a vacuum gauge; it is connected at an intake manifold vacuum source and the engine is warmed and the vacuum readings at idle condition and at accelerating engine speed up to 2000 rpm are noted and any significant decrease noted. To replace, ensure that the vehicle is upheld on jackstands, unplug the electrical connections of the oxygen sensor, remove flange bolts that connect the exhaust pipe and exhaust manifold, and hold the exhaust pipe without excessive bending of the flex pipe. Disconnect the catalyst converter with the exhaust system, clean the mounting flanges, and put in place fresh gaskets, taking care not to overload the mountings and having them perfectly aligned and devoid of stress when tightening the clamps during re-installation.
Related Volkswagen Parts
Browse by Model
Arteon Catalytic Converter Atlas Catalytic Converter Atlas Cross Sport Catalytic Converter Beetle Catalytic Converter CC Catalytic Converter Cabrio Catalytic Converter Cabriolet Catalytic Converter Eos Catalytic Converter EuroVan Catalytic Converter Fox Catalytic Converter GTI Catalytic Converter Golf Alltrack Catalytic Converter Golf Catalytic Converter Golf R Catalytic Converter Golf SportWagen Catalytic Converter Jetta Catalytic Converter Passat Catalytic Converter Phaeton Catalytic Converter Quantum Catalytic Converter R32 Catalytic Converter Rabbit Catalytic Converter Rabbit Convertible Catalytic Converter Routan Catalytic Converter Scirocco Catalytic Converter Taos Catalytic Converter Tiguan Catalytic Converter Tiguan Limited Catalytic Converter Touareg Catalytic Converter Vanagon Catalytic Converter