×
- Hello
- Login or Register
- Quick Links
- Live Chat
- Track Order
- Parts Availability
- RMA
- Help Center
- Contact Us
- Shop for
- Volkswagen Parts

My Garage
My Account
Cart
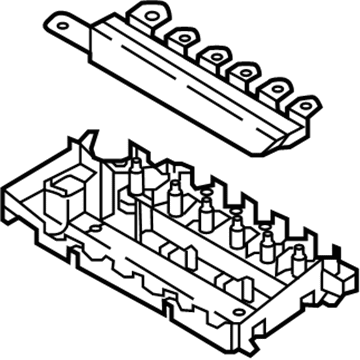
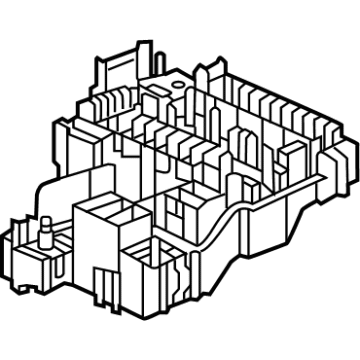
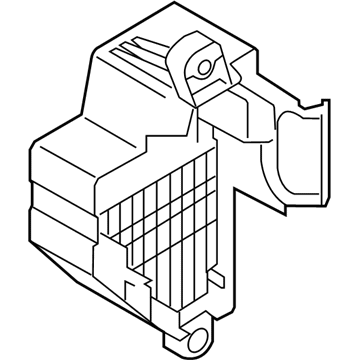
Genuine Volkswagen Fuse Box
Fuse Holder Box- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
45 Fuse Boxes found
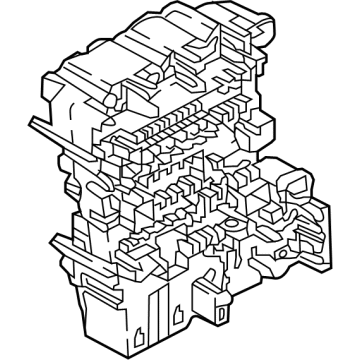
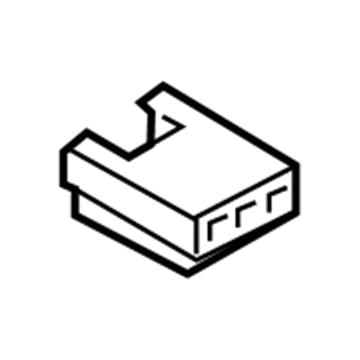
Volkswagen Junction Block Part Number: 5WA-937-615
$26.51 MSRP: $44.18You Save: $17.67 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Plate
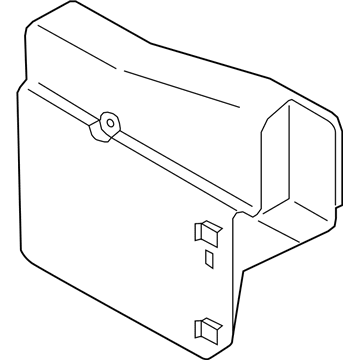
Volkswagen Fuse Box Part Number: 1H1-971-821
$27.00 MSRP: $45.00You Save: $18.00 (40%)Product Specifications- Other Name: Plate; Fuse Box
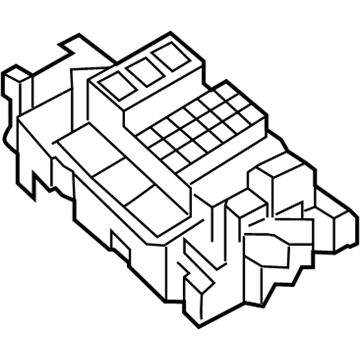
Volkswagen Fuse Box Part Number: 30G-937-548
$30.11 MSRP: $50.19You Save: $20.08 (41%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Fuse Box Part Number: 5C6-941-824-A
$19.14 MSRP: $31.38You Save: $12.24 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Fuse Box Part Number: 3D0-937-619-P
$22.31 MSRP: $36.59You Save: $14.28 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysVolkswagen Relay & Fuse Plate Part Number: 5WA-937-125-E
$34.55 MSRP: $57.58You Save: $23.03 (40%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: E Box
Volkswagen Fuse Box Part Number: 1H0-937-530
$13.04 MSRP: $21.37You Save: $8.33 (39%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Replaces: 161-937-501
Volkswagen Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: 5C0-937-125-A
$49.91 MSRP: $69.33You Save: $19.42 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Plate
Volkswagen Housing Part Number: 5Q0-907-361-D
$58.43 MSRP: $81.16You Save: $22.73 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Fuse & Relay Box
Volkswagen Housing Part Number: 5Q0-907-361-G
$58.43 MSRP: $81.16You Save: $22.73 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Fuse & Relay Box
- Replaces: 5Q0-907-361-C
Volkswagen Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: 5WD-937-125-D
$45.59 MSRP: $63.31You Save: $17.72 (28%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: E Box
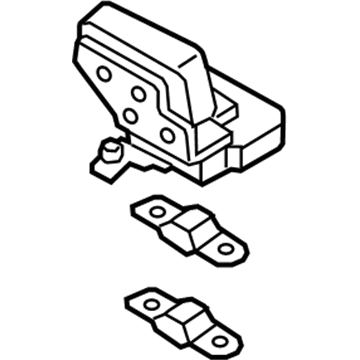
Volkswagen Relay Plate Part Number: 7L0-937-503
$69.01 MSRP: $96.65You Save: $27.64 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Plate; Relay Fuse Plate
Volkswagen Fuse Box Part Number: 1T1-937-615-B
$70.20 MSRP: $98.31You Save: $28.11 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Holder
Volkswagen Relay Plate Part Number: 7L0-937-503-A
$70.20 MSRP: $98.31You Save: $28.11 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Plate; Relay Fuse Plate
Volkswagen Relay Plate Part Number: 7L0-937-503-D
$72.58 MSRP: $101.66You Save: $29.08 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Plate; Relay Fuse Plate
Volkswagen Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: 3D0-937-499-B
$78.53 MSRP: $109.98You Save: $31.45 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Plate
Volkswagen Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: 5C0-937-125-C
$79.72 MSRP: $111.65You Save: $31.93 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Plate
Volkswagen Relay & Fuse Plate Part Number: 5Q0-937-125-G
$157.07 MSRP: $219.98You Save: $62.91 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: E Box
Volkswagen Fuse & Relay Box Part Number: 5WA-937-125-B
$111.85 MSRP: $156.65You Save: $44.80 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: E Box
Volkswagen Fuse Box Part Number: 1K1-941-824
$123.75 MSRP: $173.32You Save: $49.57 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Holder; Fuse Holder
| Page 1 of 3 |Next >
1-20 of 45 Results
Volkswagen Fuse Box
A total system failure could result from a malfunctioning Volkswagen Fuse Box, reducing driving comfort and posing a danger. It is for this reason that you should conduct regular inspections and replace such components in good time to enable your car to run smoothly and safely. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) Volkswagen Fuse Boxes are perfect for motorists because they are the best quality parts produced as per the manufacturer's specifications; hence, they perform well and are reliable too, thus helping to retain the car's initial functionality as well as safety features. At VWPartsGiant.com, our genuine Volkswagen Fuse Box supply indicates how much we care about the health of your vehicle. Additionally, our stock is vast, so every product will be easily accessible to you for finding and swapping without fear of making mistakes. With our user-friendly online catalog, it takes no time to identify the right spare part. Therefore, convenience accompanies servicing or maintaining a motorcar. You can rely on our OEM Volkswagen Fuse Box to sustain the performance of your automobile.
Volkswagen Fuse Box Parts and Q&A
- Q: How does a Fuse Box safeguard the electrical circuits and what should be considered when replacing fuses on Volkswagen Jetta?A:A combination of fuses, circuit breakers, and fusible links protect the vehicle electrical circuits, with the main fuse/relay panel being in the right-front of the engine compartment and the interior fuse/relay panel being at the left end of the instrument panel under a cover. Several different sizes of fuses are used, such as small, medium, and large, with the same design of the blade terminal, where medium and large fuses can be removed by hand but small fuses would need pliers or a fuse-puller tool of plastic. In case an electrical component fails, it is necessary to verify the fuse first with a test light to check power at the terminal ends, a broken fuse may be visibly identified by the fact that the element between the terminals is melting. It is essential to ensure that blown fuses are replaced with the appropriate type of fuse since fuses with varying ratings though may physically fit in the right fuse, are not recommended because of the particular protection requirement of any circuit. When a replacement fuse blows instantly, the cause of this problem, usually a short circuit caused by damaged wiring, should be solved before additional replacements. At least one system has switched to non- replaceable internal fuse systems or computer controlled amperage analysis where the computer will shut down the system in case the amperage goes above safe levels until the next key cycle. The use of high amperage circuits, as are found in the underhood fuse/relay box, should be carefully replaced with the same kind of fuse, and problems reoccurring on these circuits ought to be troubleshot prior to a replacement being made.
- Q: How does a Fuse Box safeguard the electrical circuits and what should be considered when replacing fuses on Volkswagen Passat?A:Several types of fuses, circuit breakers, and fusible links are used to provide protection to the electrical circuits of the vehicle, and the fuse panel inside the instrument panel is positioned at the left end of the instrument panel and the main fuse/relay panel is located immediately below it. A fuse is supposed to protect a given circuit which is indicated on the fuse panel. Fuses used in the fuse blocks come in different sizes, small, medium and large with identical blade terminals design, and five fuses that are referred to as metal that are located in the engine compartment fuse panel. Medium and large fuses may be pulled out, but small ones must be pulled out with pliers or a plastic fuse-puller device. The metal fuses are to take heavy loads and in case the metal strip melts because of overloading, it is easily noticeable but during replacement; one is expected to disconnect the battery. In the event of the failure of an electrical component, it is good to first, check the fuse and the most important option is to utilize a test light to see whether there is power at the exposed terminal ends of each fuse, and this can also be achieved by visual inspection. It is also essential that blown fuses are not replaced by incorrect type because fuses of various ratings might be physically compatible but should not be used interchangeably in order to obtain adequate protection. In case a replacement fuse blows instantly, it is not to be replaced once again before the cause of the problem which may also be a short circuit caused by a broken or worn out wire is eliminated.
Related Volkswagen Parts
Browse by Model
Arteon Fuse Box Atlas Cross Sport Fuse Box Atlas Fuse Box Beetle Fuse Box CC Fuse Box Cabrio Fuse Box Corrado Fuse Box Eos Fuse Box GTI Fuse Box Golf Alltrack Fuse Box Golf Fuse Box Golf R Fuse Box Golf SportWagen Fuse Box ID.4 Fuse Box Jetta Fuse Box Passat Fuse Box Phaeton Fuse Box R32 Fuse Box Rabbit Fuse Box Taos Fuse Box Tiguan Fuse Box Tiguan Limited Fuse Box Touareg Fuse Box e-Golf Fuse Box